issue date:2016-3-31 15:35:44 visit frequency:3156
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of a mirror composed of multiple thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickness of the dielectric layers, one can design an optical coating with specified reflectivity at different wavelengths of light. Dielectric mirrors are also used to produce ultra-high reflectivity mirrors: values of 99.999% or better over a narrow range of wavelengths can be produced using special techniques. Alternatively, they can be made to reflect a broad spectrum of light.
Dielectric mirrors function based on the interference of light reflected from the different layers of dielectric stack. The manufacturing techniques for dielectric mirrors are based on thin-film deposition methods. Common techniques are physical vapor deposition, chemical vapor deposition, ion beam deposition, molecular beam epitaxy, and sputter deposition. Common materials are magnesium fluoride, silicon dioxide, tantalum pentoxide, zinc sulfide, and titanium dioxide.
|
Dielectric Mirrors |
||
|
Material |
N-BK7, UV Fused Silica, other optical glass |
|
|
Dimension Tolerance |
+0.0, -0.1mm |
|
|
Thickness Tolerance |
± 0.1mm |
|
|
Surface quality |
60/40 |
|
|
Clear Aperture |
>90% |
|
|
Flatness |
λ/4@633nm |
|
|
Parallelism |
<3' |
|
|
Bevel |
<0.25mm X 45° |
|
|
Coating |
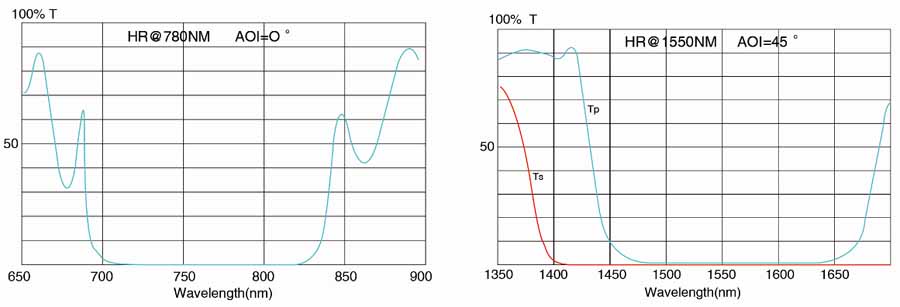
Ravg>98%@400-750nm(DielectricMirror) |
|
last:CaF2
next:Cone Lenses